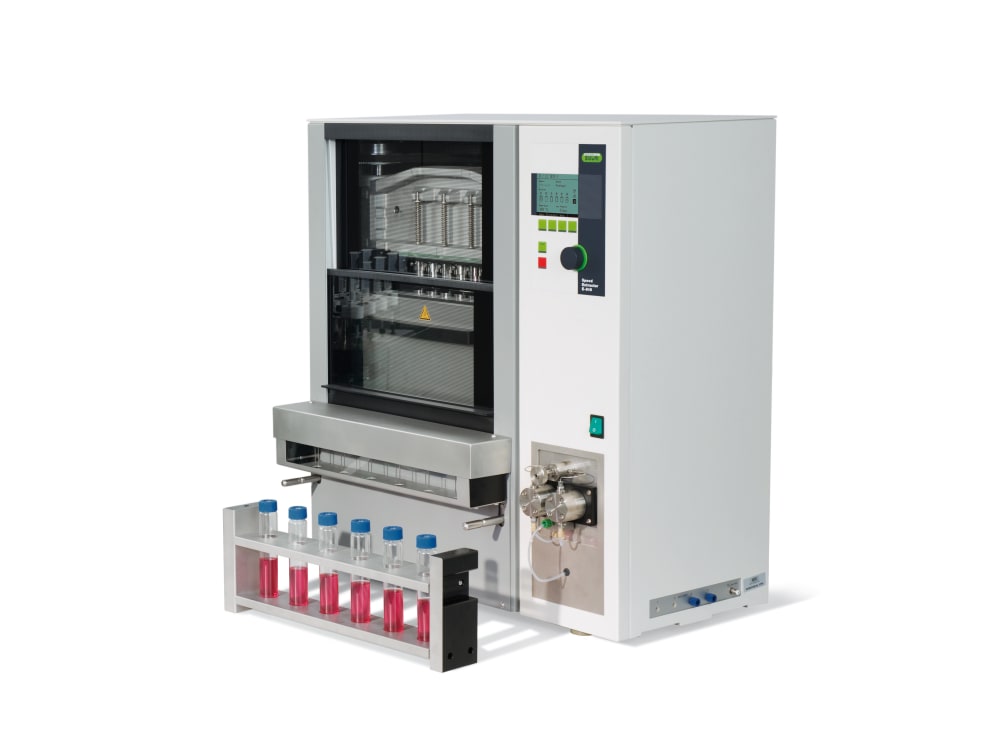
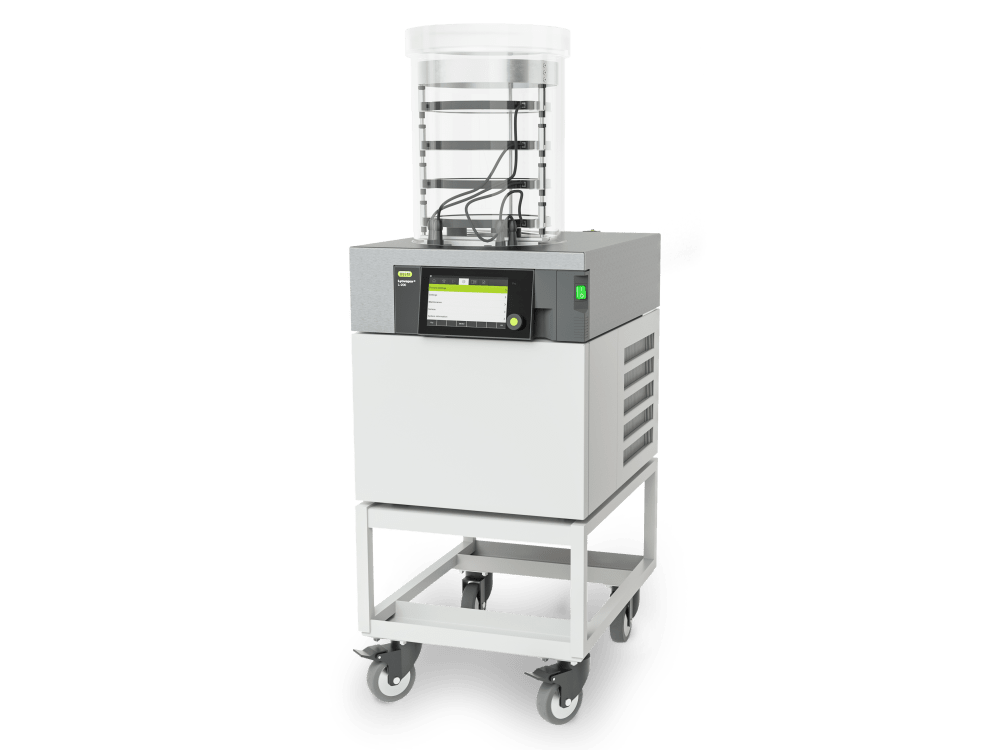
多环芳烃(PAHS)是由许多芳香环组成的氢和碳的有机化合物。有150多个此类化合物,其中包含两个或多个苯环,例如萘(NAP)和蒽(ANT)。PAH是非极性和亲脂性的,主要在天然来源(例如杂酚油)中发现。它们也通过有机物的不完全燃烧产生。如今,PAH污染的主要来源是由人类活动引起的,并且在全球各地不同。大多数PAH通过燃烧和热解的过程通过大气进入环境。由于空气中的PAH以及在受污染水域的鱼类中的沉积,在各种食物中发现了PAH。在某些食物制备方法(例如炭烧,烧烤,烤和油炸)中,还形成了PAH。呼吸道和皮肤是受人体PAH最受影响的两个器官。常见的症状包括太阳皮炎,痤疮皮炎和表皮炎。 Many countries and regions have regulations to prohibit and detect the compounds of PAHs.In 1982, the American Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) introduced 16 representative PAHs as priority compounds for the monitoring of pollutants5. In 2016, the Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China published a new series of decrees and regulations regarding PAHs in environmental areas such as soil, sediment, sludge and air. The regulations clearly list the detection methods and value limits for PAH compounds in different applications. In the regulations HJ 783-2016 and HJ 805-2016, they recommend the extraction of a solid sample using the Pressurized Fluid Extraction method (PFE, also known as Pressurized Solvent Extraction PSE) of lyophilized samples prior to analysis by GC-MS.